Technologies Used for Waste water Treatment In Kuwait
Eng. Mohammoud Khaled KAram
Introduction to Kuwait
* State of Kuwait has a land area of 17,818 km2.
* The population of Kuwait is 3.6 million (June 2010).
* About 98% of population live within Kuwait Metropolitan Area, 810 km2 or 4.5% of total area.
* Kuwait is the only country in the world without natural lakes or rivers.
* Climate of Kuwait is dry, hot desert and annual evaporation far exceeds rainfall average of 125mm per year.
Introduction to Kuwait
* Kuwait is part of a large regional desert situated at low altitude.
* Average temperature is 33°C, but drops as low as -3°C in January. Maximum temperature is 52°C.
* Annual rainfall is between 25 mm and 175 mm, most of this falling between October and March. Winter also brings fierce dust storms.
* The harsh climate and the rapid growth of demand on fresh water resources due to increasing urbanization and agricultural projects, leads to search for alternative sources of water.
* Population increase results in growing volumes of municipal wastewater. This leads to health and environmental problems if not treated properly.
* Kuwait is one of the highest consumer of fresh water in the world, the consumption of fresh water per capita is 500 liters per day. The fresh water is produced from desalination of sea water where the water production reached about one million cubic meters per day.
Competence of The Ministry of Public Works MPW
Study and design, construction and maintenance: 
* Roads and bridges.
* Infrastructure for residential areas.
* Rain and sanitation networks and facilities.
* Various governmental facilities and buildings.
Sanitary Engineering Sector
The sanitary engineering sector in the Ministry of Public Works is in charge of:
* Wastewater Management.
* Preparation of technical studies.
* Technical assistance to develop the facility.
* Construction of all projects related to the renewal of sewerage systems.
* Improving the performance of transfer stations and water treatment.
* Raising the efficiency of capacity of the networks to meet the rates of population growth.
Pollutants in Raw Sewage
* Raw domestic sewage consists of physical and chemical compounds, microbes and viruses. 
* The physical compounds can be divided into 99.9% water and 0.1% solids (pollutants). The solids can be divided into dissolved solids (75% - 65%) and suspended solids (25% - 35%) which are 50% settle-able suspended solids and 50% non settle-able solids.
* The chemical compounds can be grouped into 30% inorganic compounds such as salts, metals, grit and sand.
* Remaining 70% are Organic Compounds such as fats, carbohydrates and proteins.
WATER RESOURCES
* Desalination
* Ground water
* Water Reuse
Desalination in GCC
* The installed desalination capacity exceeds 3000 million m3 yearly.
* Representing about 50% of World’s desalination capacity.
* Covers about 90% of the domestic/industrial demand.
* GCC capital investments for past two decades is us $ 16 billion.
* GCC needed investments for coming 20 years is about us $ 50 billion.
Ground Water
* Provides Majority Of Total Water Demand in GCC.
* Excessive withdrawal from aquifers in the past years at a rate exceeding the natural replenishment led to :
- Depletion.
- Increase in the capital and operational cost.
- Increase in salinity.
Waste Water Reuse
* Solves two problems :
- Environmental Pollution.
- Water Resource Deficit.
- Available in different alternatives: Secondary, Tertiary, & RO.
* Various applications depending on treatment level.
Sewage Treatment 
* Sewage treatment is traditionally divided into the following stages:
- Primary treatment, which is based on physical operations such as screening, de-gritting and odour control.
- Secondary treatment, which is biological treatment using activated sludge and performed in bioreactors (aeration tanks) and classifiers.
- Tertiary treatment, which applies physical and chemical operations such as filtration and chlorination.
- RO treatment, which applies ultra and micro filtration using Reverse Osmosis.
- Sludge treatment, which applies physical and biological treatment operations such as thickeners and digesters (aerobic).
The present & future strategies for the sanitary sector
Renovation of old network as follows: 
A. Replacement of decaying pipes (asbestos) with a better quality pipes that have longer life time which can reaches 50 years-and-over, so can resists the aggressive soil from outside and the highly polluted sewage from inside.
B. Replacing the old concrete manholes with new lined manholes which can resist the aggressive nature of the gases that emissions from the sewage.
C. Improving the slope of the sewer pipes in the whole network to gain the following :
1. Faster flow inside the pipe (self cleaning).
2. Deleting old lifting and pumping stations to reduce the operation , maintains and odor problems.
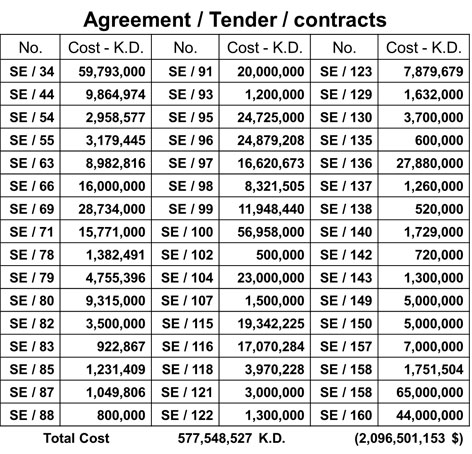
3. Constructing new 5 huge pumping stations which will replace the 57 old pumping stations and there related lifting stations.
New Deep Tunnel Sewers and Pumping Stations
Four main sub-catchments will be served by the new system
1. Mishref PS – Serves areas to the south and east of the City centre and transfers sewage to Ardiya PS and on to Sulaibiya Sewage Treatment Plant (STP).
2. Riggae PS – Serves areas to the north and east of the city centre and also transfers to the Ardiya/Sulaibiya system.
3. Egaila PS – Serves the south of the Kuwait Municipal Area and transfers sewage to the Riqqa STP.
4. Jahra PS – Serves the Jahra catchment and will transfer sewage to Kabed STP.
Strategic Projects Currently Being Delivered
* Agreement No. EF/S/121 Kuwait Sanitary Master Plan. This project will deliver a strategy for the development of Kuwait’s sanitary system until 2045. The Master Plan will incorporate strategy related to the development of sewers, pumping stations and sewage treatment plants, as well as the interaction with final effluent distribution and sludge management.
* Agreement No. EF/S/83 Rehabilitation and Improvement of Sewerage and Infrastructure in Jleeb Al-Shuyoukh, Phase 13.
Strategic Projects currently being Tendered
Agreement No. EF/S/87 for Rehabilitation and Improvement of Sewerage and Infrastructure in Al-Andalus, Gernata, Sabah Al-Nasser Areas, Phase 15.
NEW SEWAGE NETWORK
Sewage Treatment Plants in Kuwait
- Riqqa STP.
- Sulaibiya STP.
- Al Khiran & Wafra STP.
- Umm Al Hayman STP.
- Jahra STP.
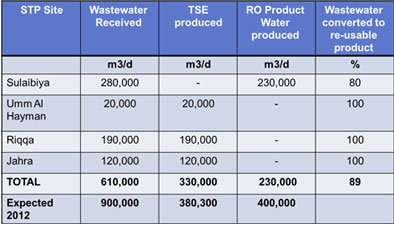
Jahra STP (Tertiary) 
* Treatment capacity 65,000 m3/day now treating 120,000 m3/day.
* Sewage to be transferred to Kabed STP from 2011.
Riqqa STP (Tertiary)
Treatment capacity 180,000 m3/day, currently receiving 220,000 m3/day. Under current Master Plan, sewage flows will be transferred to new Umm Al Hayman STP by 2015.
Umm Al Hayman STP (Tertiary) 
* Current treatment capacity of 27,000 m3/day and treating 20,000 m3/day.
* Under the current Master Plan this site will be expanded to treat up to 650,000 m3/day.
* Extensive Treated Sewage Effluent (TSE) network proposed for expanded works.
Sulaibiya STP, Reverse Osmosis
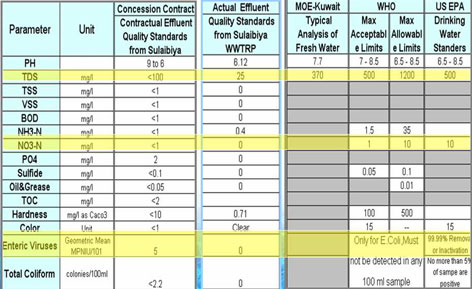
* Sulaibiya is the largest STP in the world that uses Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology as an advanced treatment for waste water.
* Treated wastewater produced is potable water quality standard and it treats 425,000 m3/day. The plant could be further expanded to treat a maximum of 600,000 m3/day.
Quantity of Treated Wastewater, 2010
WATER PARAMETERS
Estimated costs of water production in Kuwait - 2009
* Tertiary treated waste water 1.73 $ / 1000 IG
* R.O treated waste water 2.95 $ / 1000 IG
* Freshwater 17.51 $ / 1000 IG
* The subsidize price of the sale of water to the consumers
* Tertiary treated waste water 0.35 $ / 1000 IG
* R.O treated waste water 0.70 $ / 1000 IG
* Freshwater 2.77 $ / 1000 IG
Characteristics of treated wastewater used for Irrigation
The quality of treated wastewater used for irrigation in agriculture and landscaping falls within the standard limits laid down by Kuwait EPA and Kuwait MPW.
* Sulaibiya recycling plant is designed to comply with Kuwait EPA standards, that are in line with other agricultural water reuse standards such as USEPA standard.
* Product Water contains zero bacteria count.
* Product water contains lower levels of organics, solids and ammonia than those required by potable water standards.
Reuse of Treated Wastewater
* Treated wastewater (TSE) provides both moisture and nutrients for the growth of plants and other vegetation.
* Reuse of treated wastewater for irrigation and landscaping has proved to be an important and alternate source for irrigation and other uses in Kuwait.
* The volume of wastewater is estimated to be 70 to 80 per cent of the potable water consumption by the population.
* Treated wastewater is available to different standards in Kuwait; Tertiary & RO Product Water.
Uses of Treated Wastewater
* Government of Kuwait is committed to make urban and suburban areas greener and to encourage Agricultural Projects such as:
* Beautification all over Kuwait with Landscaping.
* Crops and Alfalfa Locations :
- Al Wafra Farms (RO) - (Crops).
- Al Abdally Farms (RO) - (Crops).
- Al Mutahida (Tertiary) - Alfalfa.
- Al Rabya (Tertiary).
- Artificial lagoons: Um-Al Ramam Lake.
* Two Golf Courses, one built to International PGA Standards.
Treated Wastewater Usage in Kuwait 
* Golf Courses.
* Golf course/Race track.
* Alfalfa Farms.
* Crops.
Financial Models for Future Projects, Private Sector Involvement
* New Umm Al Hayman STP procured through PPP.
* Ultimate capacity of new STP will be 650,000 m3/day.
* Cost of new Umm Al Hayman STP and related works is about KD 450 million (US$ 1.6 Billion).
* Related Works includes comprehensive TSE Network.
* Transaction Advisory Services being tendered now.
* New STP and TSE Network will be operational by 2015.
The Environmental Affairs Department (EAD)
The State of Kuwait extends the great efforts in environmental protection field to reduce the impact of pollutants on human health, environment, natural resources and public property. Some of main tasks of EAD
* Regular follow up of the complete sewerage system to assess the level of pollution and find the best solutions for environmental problems.
* Co-ordination with EPA regarding Environmental Problems related to sanitary sewers.
* Periodical monitoring on the emergency outlets of the storm water networks.
* Monitoring the quality of ground water to assess the level of pollution before discharge into storm network at new construction site till the dewatering is completed at those site.
* Injecting chemical or biological products in emergency cases with the help of the laboratory and environmental research section.
* Perform all necessary experiments and analyse results that are requested by the other sections of (EAD ) , sanitary administration sector.
In Conclusion
Water Reuse represents a Genuine Water Resource that Makes Perfect Environmental and Economic Sense:
* The State of Kuwait currently Reuses all its treated wastewater.
* Major new wastewater treatment plant is planned for Umm Al Hayman.
* Umm Al Hayman STP includes an extensive TSE network in the south in order to ensure total Reuse of all TSE produced.
* Private sector involvement in the delivery of Umm Al Hayman STP will be sought through PPP.
* We in the Ministry of Public Works, in cooperation with the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (through a memo- randum of understanding which was signed in 2010) we hope to achieve many of the projects that concern the country and its citizens (such as the full use of treated waste water and sludge, establishing Quota system for distrubuting the treated waste water).
Reference:
Proceeding Of the Workshop on "Appropriate Waste water Reclamation and Reuse Technologies for Aride Environments"








